

 Contact
Contact
About Direct Drive Motors and μDD Motor
Direct drive motors couple the rotor directly to the load. With no gears or belts, the actuator avoids gear backlash, runs quieter, and needs less maintenance. Final accuracy and settling depend on encoder resolution, structure rigidity, and tuning.
A DD motor couples the rotor directly to the load—no reducer, no belt. That removes gear backlash and common gear/belt noise sources. As with any actuator, performance should be validated on the actual mechanism.
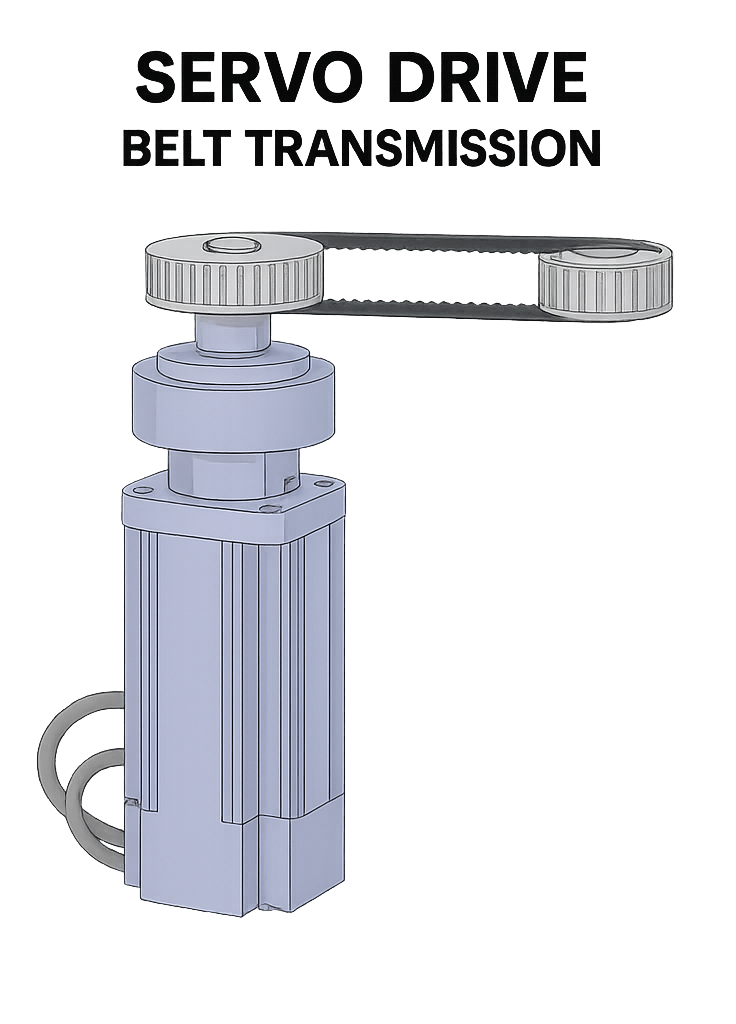
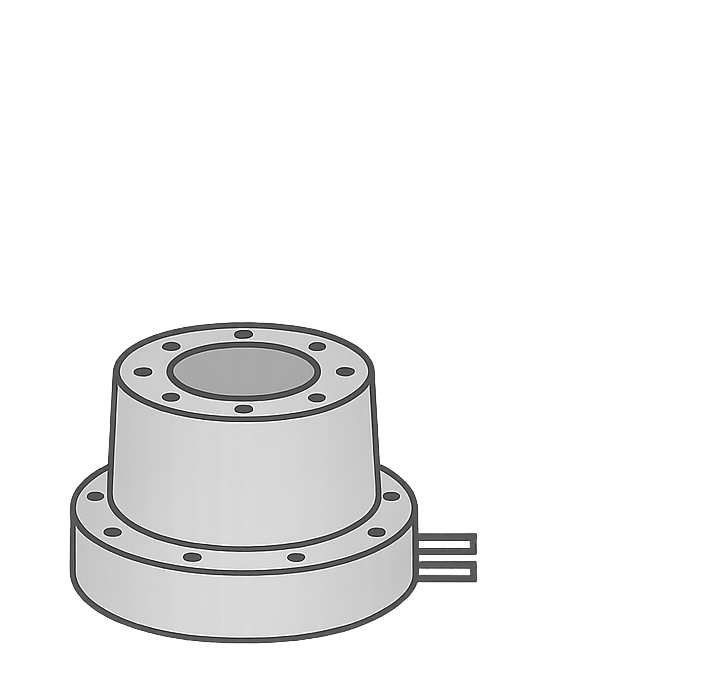
Direct coupling eliminates gearbox play. Result still depends on encoder, rigidity, and tuning.
Fewer meshing parts reduce mechanical and acoustic noise sources.
No reducer lubrication or belt tensioning tasks.
Hollow shaft eases routing for cables, vacuum, or optics.
Well-suited to indexing, alignment, and gimbals.
Current/speed/position loops act directly on the load.
MTL’s μDD motors are hollow-shaft direct-drive actuators designed for compact equipment. They integrate high-resolution feedback and support tuning with the MTLParam app. μDD is used in alignment axes, rotary modules, and small precision mechanisms where low noise, clean routing, and repeatability are important.
| Hollow shaft | Route cables, air, or vacuum lines through the center (within allowed loads). |
|---|---|
| Encoders | Incremental or absolute options vary by series; see each model page for formats and resolution. |
| Drivers | MTL drivers (EtherCAT/analog/I/O) and several third-party platforms are supported. |
| Tuning | Auto-tuning plus manual recipes with logging for traceability (MTLParam). |
| Safety | Use STO; add a brake for gravity-loaded axes if required by your tool. |

Each series page includes Specifications, Dimensions & Wiring, Cables, MTLParam App, and Support.
Very small hollow-shaft DD for instruments and tight spaces.
Ultra-compact hollow-shaft DD for micro stages.
Versatile sizes for indexing, scanning, and alignment.
Higher torque for rotary modules and wafer-handling subsystems.
Large diameter, large through-shaft for process utilities.
Rotary module with large hollow shaft for equipment modules.
Step 1 — Load & motion profile. Inertia, peak/continuous torque at speed, duty cycle, settle time, holding torque, environment.
Step 2 — Hollow-shaft routing. What passes through the axis (cables, air, vacuum, optics).
Step 3 — Driver & control. MTL driver or compatible platform (EtherCAT / analog / I/O).
Step 4 — Mounting & safety. Rigidity, backdrivability, brake/STO strategy, emergency stop.
| Controller / Drive | Interface | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| MTL driver family | EtherCAT / analog / digital I/O | Auto-tuning, manual tuning recipes, MTLParam app. |
| Mitsubishi MELSERVO-J5 | Encoder & I/O per model | Common in factory automation; wiring options available. |
| Panasonic MINAS series | Encoder & I/O per model | Widely used in equipment and robotics projects. |
Semiconductor equipment
Back-end assembly, inspection, wafer transfer, rotary chucks, aligners. Benefits: no gear backlash, quiet, large through-shaft for vacuum lines.
Optics & photonics
Laser attenuators, pan-tilt gimbals, filter wheels, precision stages. Benefits: smooth low-speed rotation, minimal mechanical noise.
Life sciences
Benchtop instruments, automated sample handling. Benefits: compact actuator, clean cable routing through hollow shaft.
Robotics
Compact joints and rotary modules. Benefits: high torque at low speed, simplified wiring through the axis.
Metrology & inspection
Indexing stages, rotary calibration fixtures. Benefits: direct coupling can improve repeatability when the structure is rigid.
R&D & universities
Haptics rigs, novel mechanisms. Benefits: backdrivable mechanics, fine control when tuned correctly.
Gear trains have measurable backlash. Direct drive has no gear backlash because there is no reducer.
Gears and belts add mesh/slip noise. Direct coupling removes those sources; remaining noise is mainly EM and bearing related.
Reducers require lubrication/inspection; direct drive removes that task. Bearings still follow normal life calculations.
Gearless design reduces wear particles at the actuator compared with geared transmissions.
Use STO and specify brakes for gravity-loaded axes.
Ask about CE/RoHS and any documentation required for your region or OEM process.
| Item | Motor + gear | μDD Motor |
|---|---|---|
| Backlash | Present (mechanical play) | None (no reducer) |
| Space | Often larger footprint | Compact layout |
| Noise | Gear whine, friction noise | Lower (no gear mesh) |
| Maintenance | Lubrication / wear parts | Minimal (bearings remain) |
| Accuracy | Limited by gearbox play | Depends on encoder, rigidity, tuning |
| Cable routing | External around reducer | Through the hollow shaft |
| Cleanroom | Higher particles | Fewer wear particles at actuator |
Dimensions & Wiring
Connector pinouts, cable part numbers, mounting drawings on each model page.
Open μDD lineupMTLParam App
Setup, auto-tuning, and logging. See guidance and tuning recipes on model pages.
User portalApplication cases
Wafer inversion mechanisms, compact stages, and custom hollow-shaft integrations.
Browse casesInertia, torque at speed, duty cycle, settle time, holding torque.
Hollow-shaft routing, flange pattern, through-shaft loads, cable paths.
Drive interface (EtherCAT/analog), STO/brake strategy, homing/absolute.
What is a direct drive motor?
How is μDD different from a servo with a reducer?
Does direct drive always settle faster?
Can I route vacuum or cables through the center?
What encoder types are available?
Which drivers are compatible?
Do I need a brake?
What about torque ripple?
Is backdrivability a problem?
How quiet is it?
How do I size a μDD motor?
What maintenance is required?
Can μDD replace my current geared motor 1:1?
Do you support on-site tuning?
Mechanical play in a transmission; appears as lost motion. Direct drive removes gear backlash by eliminating gears.
Periodic torque variation driven by motor/drive factors. Verify on your mechanism with logs.
Through-hole geometry that allows routing through the axis within specified limits.
Selection support
We help choose the right μDD model and driver based on load inertia, torque at speed, duty cycle, and motion profile.
Tuning support
Start with auto-tuning, then refine manually. Remote or on-site support available with log sharing for traceability.
Warranty
Initial defects covered within one year after first use and within 1.5 years after delivery. After-sales includes repair and root-cause analysis.

