Active Gimbal for Precision Positioning
Technology and devices that move, fix, and hold a target at a specific position or angle with high accuracy.
Position can be controlled with micron-level precision.
Tracking system using image recognition
The subject is detected by image recognition, and a powered gimbal (active gimbal) automatically tracks and shoots the subject.
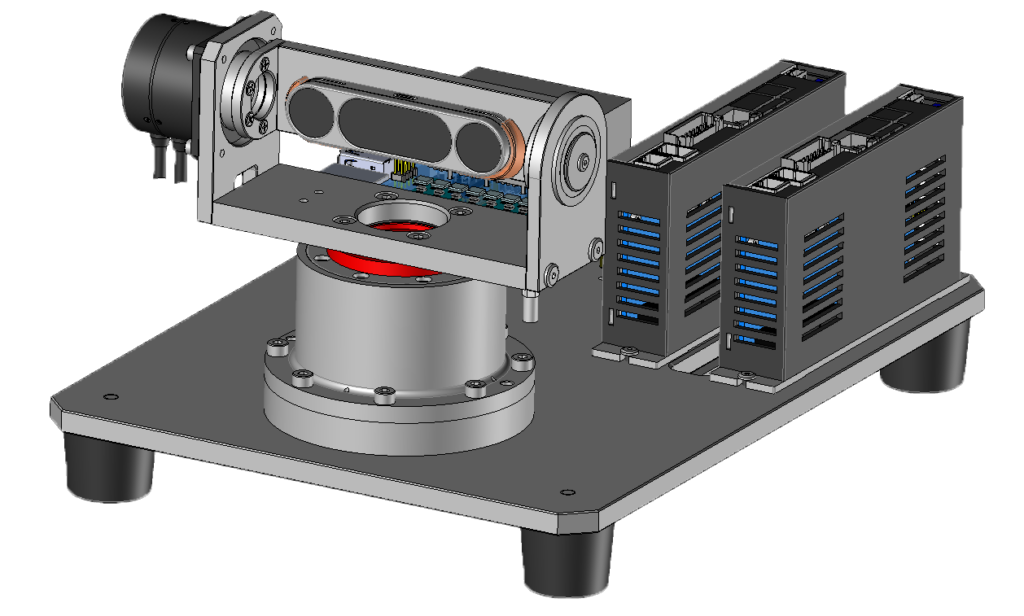
Active gimbals require high agility and responsiveness.
By using a gearless structure, weight from gears is eliminated and acceleration performance improves.
They are quiet, so the impact on audio recording is minimal.
Other industries
The requirements for precise motion, high responsiveness, and light weight pair well with compact direct-drive motors.
Other use cases include antenna gimbals for communications, and optical systems such as telescopes and laser cutters.
They can also be used for fine positioning in long-distance aerospace communications.
(Research use) High-speed tracking pan-tilt head
User: Chiba University, Namiki Laboratory
HP: http://www.em.eng.chiba-u.jp/~namiki/









