Direct Drive Wafer Lifter
Use cases: etching tools, probers


Challenge: dead space
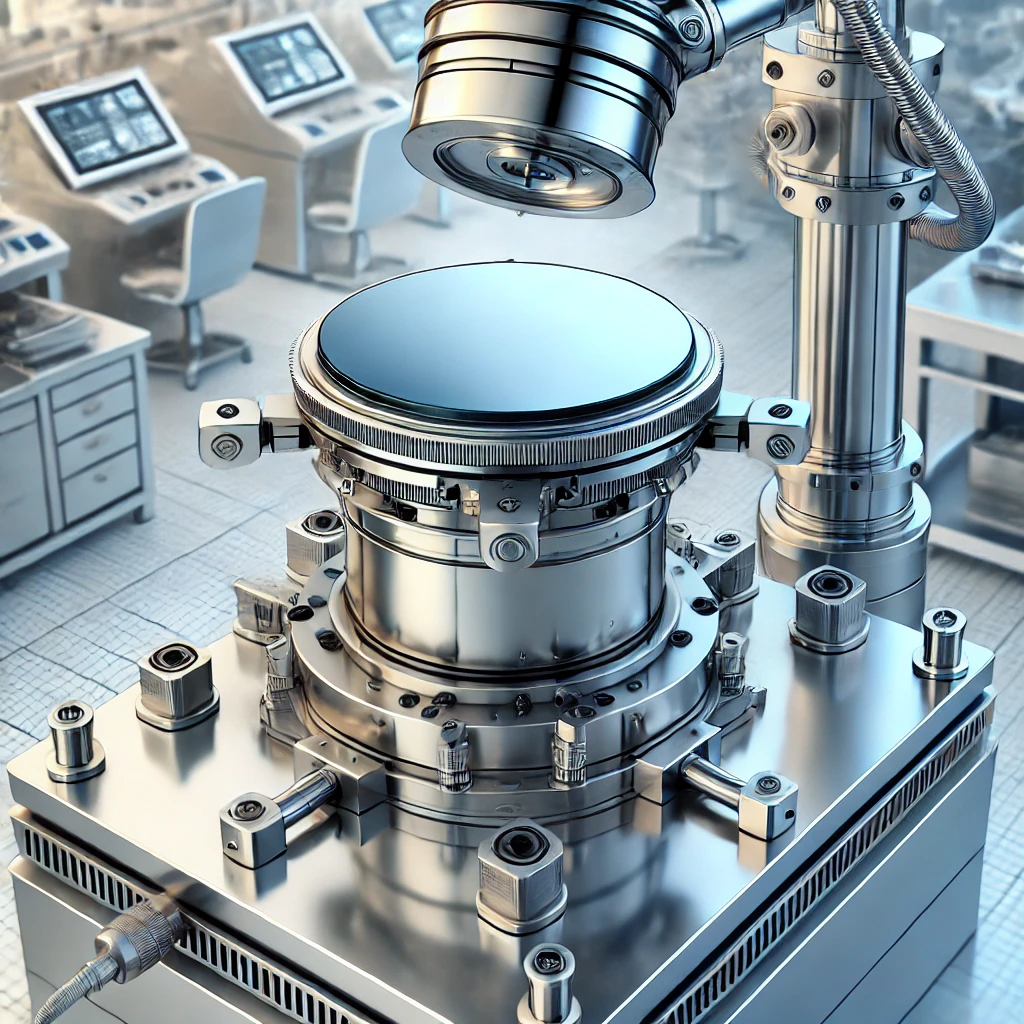
To raise and lower the lifter, space was needed for the motor itself and for parts such as gears and belts that convert rotary motion into vertical linear motion.
These surrounding parts increased the required space.
As a result the lifter tended to become bulky, creating dead space,
and the overall equipment size often grew larger.
Solution and DD motor benefits
Minimize equipment height
Pass a ball screw through the hollow shaft to lower the overall height of the system.
This reduces installation space and enables compact equipment.
Ideal when high-precision motion in tight spaces is required.
Anomaly detection
By feeding back motor current, abnormal conditions can be detected.
This reduces wafer-damage risk and improves maintenance and cost performance.
Example: early detection of overloads or wear-related faults
Benefit: minimize downtime and maintain productivity
Models used
| Model name | Product name | Remarks | |
| 1 | MDH-2018-36KE (tip section) | Ultra-compact hollow direct-drive motor | Outer diameter φ21 mm, hollow inner diameter φ2.6 mm Resolution 144,000 C/R Peak torque 130 mN·m |
| 2 | MDH(6)-3018-108KE (middle section) | Compact, large-bore hollow direct-drive motor | Outer diameter φ40 mm, hollow diameter φ12 mm Resolution 1,296,000 C/R Peak torque 1 N·m |
| 3 | MDH(12)-4018-324KE (middle section) | Compact, large-bore hollow direct-drive motor | Outer diameter φ70 mm, hollow diameter φ25 mm Resolution 2,592,000 C/R Peak torque 3 N·m |









